Enforcement Directorate | Enforcement Directorate Lawyers
Legal Support for Matters Involving Enforcement Directorate(ED)
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is a law enforcement agency that functions under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, and Government of India. The agency is responsible for enforcing economic laws and fighting financial crimes in the country. Matters pertaining to ED are serious in nature and require expert legal guidance to navigate the complex legal system. Bhatt & Joshi Associates, the best law firm in Gujarat, Ahmedabad, provides legal services and litigation support to clients in matters related to ED.
Functions of ED and its Constituent Law
The ED was established in the year 1956 and derives its power from the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) and Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA). The primary function of the ED is to investigate and prosecute cases of money laundering, illegal foreign exchange transactions, and other financial crimes. The agency is also responsible for the confiscation of proceeds of crime and properties involved in money laundering.
The seriousness of Matters Involving ED
Matters involving ED are serious in nature and can have severe consequences for individuals and businesses. The agency has the power to freeze bank accounts, attach properties, and even initiate criminal proceedings against individuals and entities involved in financial crimes. As such, it is crucial to seek expert legal guidance to navigate the complex legal system and protect one’s interests.
Predicate Offences under PMLA and Jurisdiction of ED
The PMLA specifies certain “predicate offences” that are considered as the basis for money laundering. These offences include terrorism, human trafficking, narcotics smuggling, and more. The ED has jurisdiction over cases involving predicate offences and can initiate investigations and take action against those involved.
Predicate offences under PMLA and FEMA
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) is an Indian law enacted to prevent money laundering and to provide for the confiscation of property derived from or involved in, money laundering. The act was passed in 2002 and is enforced by the Enforcement Directorate (ED). Money laundering is the process of concealing the proceeds of illegal activities such as drug trafficking, terrorist financing, bribery, corruption, etc., to make it appear as though the proceeds were obtained from legitimate sources. Predicate offences are the underlying criminal activities that generate illegal proceeds that are then laundered.
- Some examples of predicate offences under PMLA include drug trafficking, human trafficking, smuggling, counterfeiting, fraud, corruption, terrorism and terrorist financing, among others. Offences under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) are one amongst many predicate offences under PMLA Act, and it is an Indian law that regulates foreign exchange and payments between India and other countries. The act is enforced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and the main objective of the act is to facilitate external trade and payments and promote orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange markets in India.
- Under the PMLA, the ED has the power to investigate and prosecute cases related to money laundering. The ED has jurisdiction to investigate cases under the PMLA where the proceeds of the crime involved in the predicate offence are equal to or more than Rs. 30 lakhs. The ED also has jurisdiction to investigate cases of foreign exchange violations under FEMA.
At Bhatt & Joshi Associates, we offer litigation support services to our clients who are facing legal issues related to FEMA and PMLA. Our team of experienced lawyers can assist our clients in understanding the legal framework and procedures under these laws, as well as representing them before the appropriate forums for hearing and adjudication of their cases. We also provide legal advisory services to clients on compliance with FEMA and PMLA to avoid legal issues in the future.
Original and Appellate Forums under PMLA
The PMLA provides for original jurisdiction to the Adjudicating Authority for matters related to the confiscation of properties and the Special Court for trial of offences. The appellate forums under the PMLA include the Appellate Tribunal, High Court, and Supreme Court. It is important to seek expert legal guidance to navigate the various forums and ensure the best possible outcome for one’s case.
Litigation Support Services by Bhatt & Joshi Associates
At Bhatt & Joshi Associates, we provide comprehensive litigation support services to our clients in matters related to ED. Our team of experienced lawyers can assist our clients in filing and defending cases, preparing necessary documentation, and representing them before the appropriate forums. We also provide legal guidance to our clients to ensure compliance with the relevant laws and regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, matters related to ED require expert legal guidance and support to navigate the complex legal system and protect one’s interests. Bhatt & Joshi Associates, the best law firm in Gujarat, Ahmedabad, provides legal services and litigation support to clients in matters related to ED, ensuring the best possible outcome for their case.
Equal justice under law is not merely a caption on the facade of the Supreme Court building, it is perhaps the most inspiring ideal of our society.
Get in touch with Best Enforcement Directorate Lawyers in Ahmedabad
Frequently asked questions
1. When should I consider hiring a civil lawyer?
You should consider hiring a civil lawyer when facing legal disputes related to contracts, property, personal injury, family matters, or any non-criminal matter where you need legal advice or representation.
2. What is a civil lawyer?
A civil lawyer represents clients in non-criminal legal matters, dealing with disputes between individuals, organizations, or both, over rights, responsibilities, and liabilities.
3. Can a civil lawyer help with contract disputes?
Yes, one of the primary areas of expertise for many civil lawyers is contract law. They can assist with drafting, reviewing, and disputing the terms of contracts.
4. How do civil lawyers differ from criminal lawyers?
While both handle legal disputes, civil lawyers focus on non-criminal cases, often involving private disputes between individuals or organizations. Criminal lawyers, on the other hand, represent individuals or the state in cases involving potential criminal penalties.
5. How are damages determined in civil cases?
Damages are determined based on the actual loss suffered, potential future losses, and sometimes, punitive measures. The nature and amount depend on the specifics of the case and jurisdictional guidelines.
6. What is the usual process of a civil lawsuit?
The typical process involves the filing of a complaint, response from the other party, discovery (exchange of relevant information), negotiations, potential settlement discussions, and if unresolved, a trial. The exact process can vary by jurisdiction.
7. Can a civil lawyer assist in mediation or alternative dispute resolution?
Yes, many civil lawyers are trained in alternative dispute resolution methods like mediation and arbitration, offering solutions outside the traditional courtroom setting.
8. How long does a typical civil lawsuit last?
The duration of a civil lawsuit varies based on the case’s complexity, the court’s schedule, and the willingness of parties to settle. It can range from a few months to several years.
Can Appellate Court Criticism Demoralise Judges? Judicial Independence and the Chilling Effect
Introduction On 13 February 2026, Justice Pankaj Bhatia of the Allahabad High Court made a remarkabl
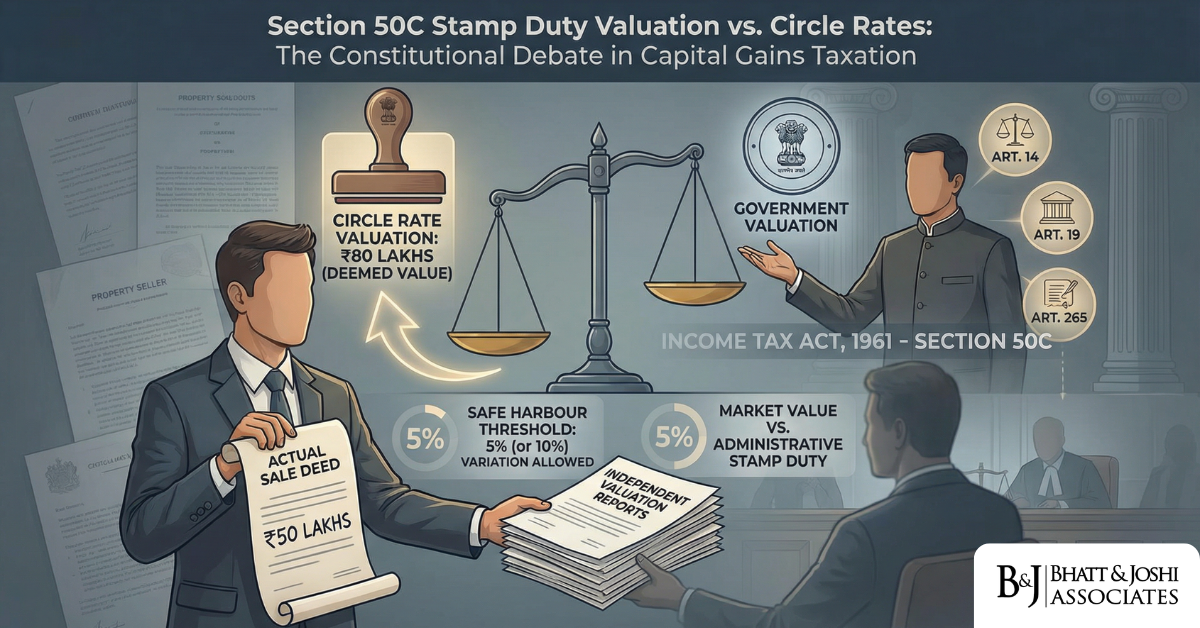
Section 50C of the Income Tax Act, 1961 Stamp Duty Valuation vs. Circle Rates: The Constitutional Validity of Deeming Fictions in Capital Gains
Introduction Few provisions in Indian income tax law generate as much sustained controversy, litigat
Livestream Donations and the TDS Gap on Creator Income in India: Why Streamers and Influencers Have No Withholding
Introduction India’s creator economy has grown into a multi-billion-rupee ecosystem, where gam
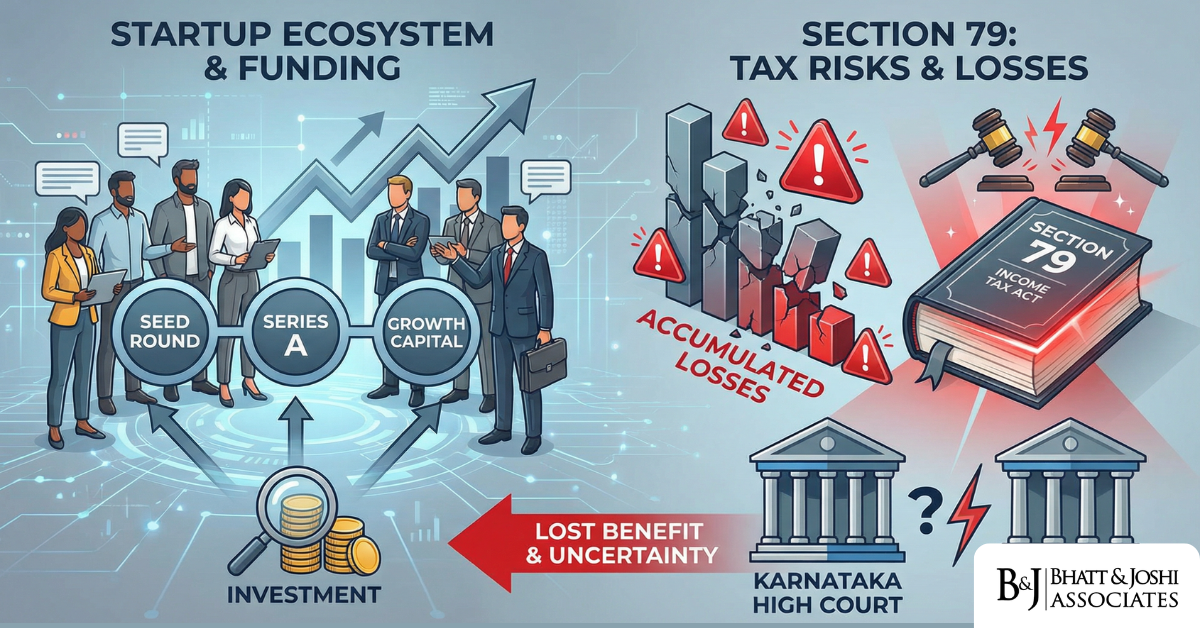
Startup Losses and Section 79 of the Income Tax Act, 1961: When Anti-Abuse Rules Kill Legitimate Restructuring
Introduction India’s startup ecosystem has grown into one of the most dynamic in the world, ye
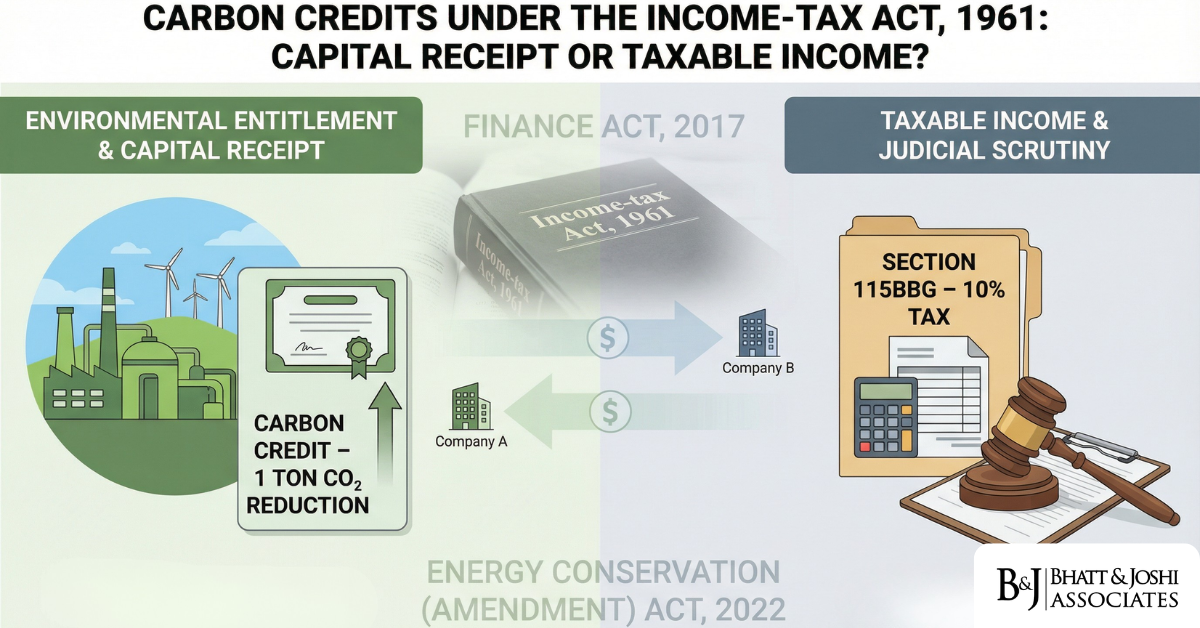
Income Tax Treatment of Carbon Credits: Asset, Income, or Capital Receipt Under the IT Act, 1961?
Introduction Carbon credits — formally known as Certified Emission Reductions (CERs) — have occu
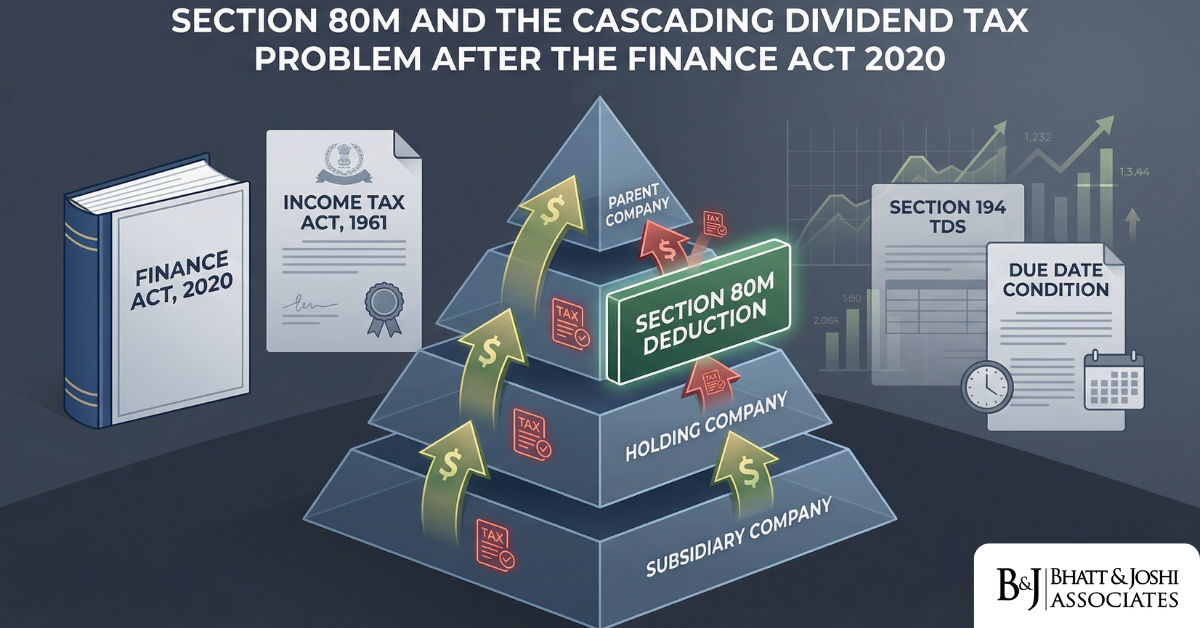
Section 80M Inter-Corporate Dividend Deduction: The Cascading Tax Problem the Finance Act 2020 Left Unresolved
Introduction When the Finance Act 2020 abolished the Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) under Section 1
TDS on Salary for Remote Employees Across Multiple Indian States Under Section 192: Compliance Challenges”
Introduction The rise of remote work in post-pandemic India has created a TDS on salary compliance c
ESOP Taxation After Exit: Why Perquisite Tax at Exercise and Capital Gains at Sale Creates Double Taxation by Stealth
Introduction Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs) are among the most powerful instruments that Indian
Crypto Losses Under Section 115BBH: Why the No-Set-Off Rule Creates an Unconstitutional Tax on Notional Gains
Introduction When the Finance Act, 2022 introduced Section 115BBH into the Income Tax Act, 1961, it
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp