Executive Summary: Legal Implications and Business Compliance Framework
The ongoing India-US trade tariff dispute, alongside bilateral trade agreement negotiations, marks one of the most significant developments in international trade law in recent years. With the July 9, 2025 deadline approaching for reciprocal tariff implementation, businesses engaged in cross-border trade face unprecedented legal and compliance challenges. This comprehensive analysis examines the legal framework governing trade disputes, WTO compliance requirements, and strategic risk mitigation strategies from a law firm perspective.
The 26% reciprocal tariff imposed on Indian goods under Executive Order 14257 has created complex legal obligations for businesses operating in the India-US trade corridor. From a legal compliance standpoint, companies must navigate an intricate web of customs law, export controls, trade remedy procedures, and contract dispute resolution mechanisms.
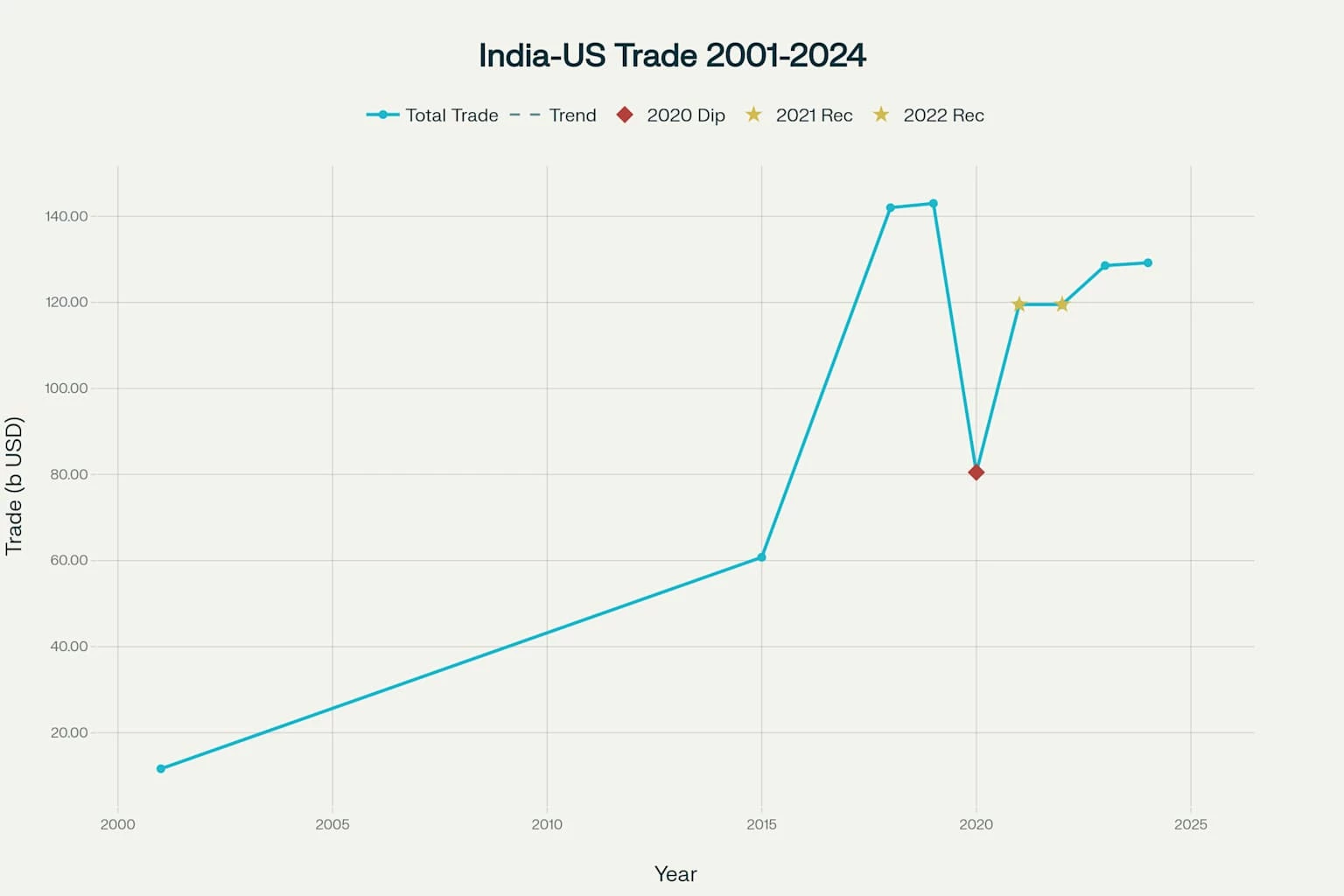
India-US Bilateral Trade Growth (2001-2024): From $11.6 billion to $129.2 billion
Understanding the Current Trade Deal Framework
The Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) Structure
The proposed India-US Bilateral Trade Agreement represents a comprehensive framework covering 19 chapters that address critical trade issues including tariffs, non-tariff barriers, customs facilitation, rules of origin, and regulatory concerns. The agreement aims to more than double bilateral trade from the current $191 billion to $500 billion by 2030.
Key Components of the Trade Deal
US Priorities:
-
Increased market access for agricultural products, particularly soya and corn
-
Elimination of India’s high tariffs on industrial goods, electric vehicles, and wine
-
Enhanced intellectual property protection
-
Greater access to India’s services sector
Indian Priorities:
-
Tariff reductions for labor-intensive industries including textiles, apparels, gems, and horticulture products
-
Restoration of Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) status
-
Elimination of US safeguard duties on steel and aluminum
-
Enhanced access for Indian pharmaceuticals and IT services
Current Trade Statistics
The bilateral trade relationship has shown remarkable growth, with US goods trade with India totaling $129.2 billion in 2024. India exported $87.4 billion worth of goods to the US while importing $41.8 billion, resulting in a trade surplus of $45.7 billion for India. This surplus has become a source of concern for US policymakers and a driving force behind Trump’s reciprocal tariff strategy.
The Nature of India-US Trade Tariff Dispute: Economic Theory and Practice
Defining Tariff Wars
A tariff war represents an economic conflict between countries where each nation levies additional taxes on the other’s exports in retaliation for similar measures. These wars typically begin when one country implements protectionist policies to shield domestic industries from foreign competition or address perceived unfair trade practices.
Trump’s Reciprocal Tariff Strategy
President Trump’s “reciprocal tariffs” approach — central to the present conflict — follows a formula designed to penalize countries with high trade surpluses against the US:
Reciprocal Tariff Rate = (US Trade Deficit with Country ÷ US Imports from Country) ÷ 2
Under this model, India was hit with a 26% tariff on exports to the US starting April 9, 2025. The move significantly intensified the India-US trade tariff dispute, prompting a temporary suspension to allow negotiations.
The Broader Tariff War Context
Trump’s tariff escalation policy has impacted 57 trading partners, raising the average US tariff rate from 2.5% to 27%. For India, the challenge lies not just in the duties but in navigating the larger geopolitical dimensions of the India-US trade tariff dispute, where legal, strategic, and economic interests are deeply intertwined.
Historical Context of India-US Trade Relations
1947–1991: From Independence to Liberalization
India-US trade relations began modestly following India’s independence in 1947. Under Prime Minister Nehru’s leadership, India pursued non-alignment and strategic autonomy, which limited economic engagement during the Cold War period. Trade volumes remained minimal, with the US providing aid through programs like PL-480 rather than engaging in substantial commercial exchange.
1991: The Turning Point
India’s 1991 economic crisis marked a transformative period. Under Finance Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh, India adopted sweeping economic reforms:
-
Tariff reduction and trade liberalization
-
Rupee devaluation and exchange rate adjustment
-
Export promotion and creation of Special Economic Zones
-
Industrial deregulation and dismantling of the License Raj
1991–2019: Accelerated Bilateral Trade
Bilateral trade rose from $16 billion in 1999 to $142 billion by 2018. Key milestones include:
-
2005: US-India Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement
-
2007: Mangoes-for-motorcycles deal
-
2010: President Obama’s $10 billion trade visit
2017–2021: First Trump Administration Trade Tensions
Trump’s first term introduced major trade friction. In 2019, the US revoked India’s GSP status, affecting over 100 Indian export products worth $945 million annually. India retaliated with tariffs on US almonds and steel, escalating tensions that laid the foundation for the current trade tariff conflict.
Legal Framework Analysis: WTO Compliance and Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Understanding the WTO Legal Architecture
The World Trade Organization’s dispute settlement mechanism serves as the primary legal framework for resolving international trade disputes. Under the Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU), member countries can challenge tariff measures that violate GATT obligations through a structured legal process.
Key Legal Principles Governing Trade Disputes:
- Most-Favored-Nation Treatment: Article I of GATT requires non-discriminatory tariff treatment among WTO members, making country-specific reciprocal tariffs legally vulnerable to challenge.
- National Treatment Obligations: Article III prohibits discrimination between imported and domestic goods once they enter the market, creating additional compliance requirements.
- Exception Clauses: Article XXI allows tariffs for national security reasons, though this remains subject to legal interpretation and challenge.
Legal Challenges to Tariff Implementation
The legal validity of reciprocal tariffs faces significant challenges in US courts. Seven lawsuits currently challenge Trump’s use of the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) to impose tariffs, with businesses arguing the President exceeded statutory authority. The US Court of International Trade is hearing these challenges, with potential Supreme Court review likely.
Critical Legal Issues Under Review:
- Presidential authority limits under IEEPA for tariff implementation
- Due process requirements for tariff classification and assessment
- Congressional oversight of executive trade powers
- Constitutional commerce clause implications
Trade Remedies and Legal Compliance Framework
Anti-Dumping and Countervailing Duty Procedures
Trade remedy laws provide legal mechanisms for addressing unfair trade practices. Companies must understand the legal standards and compliance requirements for anti-dumping investigations, countervailing duty proceedings, and safeguard measures
Legal Requirements for Trade Remedy Compliance:
- Accurate Cost Reporting: Companies must maintain detailed cost records to defend against anti-dumping allegations.
- Subsidy Disclosure: Businesses receiving government incentives must ensure proper disclosure to avoid countervailing duty liability.
- Market Share Analysis: Companies must monitor import competition and injury determinations for potential safeguard proceedings.
Export Control and Sanctions Compliance
Export control laws create additional legal obligations for businesses engaged in international trade. The Department of Commerce, State Department, and Treasury Department maintain licensing requirements for sensitive technologies and dual-use items.
Key Compliance Areas:
- Technology transfer restrictions
- End-user verification requirements
- Sanctions screening procedures
- Record-keeping obligations
Contract Law Implications and Dispute Resolution
Force Majeure and Hardship Clauses in Trade Contracts
Tariff-related contract disputes often center on risk allocation and performance obligations when trade policies change unexpectedly. Legal recourse depends heavily on existing contract language and applicable law.
Legal Remedies for Contract Disputes:
- Contractual Damages: Monetary compensation for losses due to tariff-related non-performance.
- Specific Performance: Court orders compelling contractual fulfillment despite tariff increases.
- Contract Rescission: Termination and restoration to pre-contractual position.
- Renegotiation Rights: Contractual provisions allowing adjustment for changed circumstances.
International Commercial Arbitration Framework
International arbitration provides an effective mechanism for resolving tariff-related commercial disputes. Major arbitral institutions including the ICC, LCIA, and UNCITRAL offer specialized procedures for trade disputes.
Arbitration Advantages:
- Neutral forum for cross-border disputes
- Enforceable awards under the New York Convention
- Specialized expertise in international trade law
- Confidential proceedings protecting business interests
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management Strategies
Customs Classification and Valuation Requirements
Accurate tariff classification remains critical for legal compliance and cost management. Companies must ensure proper HS code classification and customs valuation to avoid penalties and enforcement actions.
Best Practices for Customs Compliance:
- Professional Classification Review: Engage customs law specialists for complex product classifications.
- Advance Ruling Procedures: Obtain binding rulings from customs authorities on classification questions.
- Internal Audit Programs: Implement regular compliance reviews to identify potential issues.
- Documentation Standards: Maintain comprehensive records supporting classification and valuation decisions.
Supply Chain Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
Supply chain diversification has become essential for mitigating tariff risks. Companies must conduct comprehensive due diligence on alternative suppliers and manufacturing locations.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Supplier Qualification: Implement robust vetting procedures for new supply chain partners.
- Country-of-Origin Planning: Develop strategies for optimizing origin requirements under free trade agreements.
- Inventory Management: Adjust stocking strategies to minimize tariff exposure.
- Insurance Coverage: Consider political risk insurance for trade disruption protection.
Legal Implications of China Plus One Strategy
Compliance Challenges in Supply Chain Restructuring
The China Plus One strategy creates complex legal compliance issues for companies restructuring supply chains. Indian companies using Chinese components face particular challenges under the False Claims Act (FCA) when exporting to US government-related contracts.
Key Compliance Risks:
- Component Origin Disclosure: Companies must accurately represent the origin of components in government contracts.
- Quality Certification: Misrepresentation of quality standards can trigger FCA liability.
- Customs Documentation: False statements in export documentation create legal exposure.
Investment Treaty Protection and Dispute Resolution
Bilateral Investment Treaties (BITs) provide legal protection for cross-border investments affected by trade measures. Companies should evaluate treaty protections and investor-state dispute settlement options.
Investment Protection Mechanisms:
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Protection against arbitrary government actions.
- Expropriation Safeguards: Compensation requirements for regulatory takings.
- Free Transfer Rights: Protection for capital repatriation.
- Dispute Resolution Access: International arbitration for investment disputes.
Strategic Legal Recommendations for Businesses
Immediate Compliance Actions
- Contract Review and Amendment: Companies should immediately review existing contracts for tariff adjustment clauses and force majeure provisions. Legal counsel should assess contract exposure and negotiate protective amendments.
- Regulatory Compliance Audit: Conduct comprehensive reviews of customs procedures, export documentation, and classification systems to ensure legal compliance.
- Dispute Resolution Planning: Develop dispute resolution strategies including arbitration clauses and governing law selections for new contracts.
Long-term Legal Strategy Development
- Government Relations Program: Establish proactive engagement with trade authorities and regulatory agencies to monitor policy developments and participate in rulemaking.
- Legal Technology Integration: Implement compliance management systems for automated monitoring of regulatory changes and documentation requirements.
- Cross-border Legal Coordination: Develop coordinated legal strategies across multiple jurisdictions to optimize compliance and minimize regulatory conflicts.
Sector-Specific Legal Considerations
Information Technology and Services
IT services companies face unique legal challenges related to data localization requirements, intellectual property protection, and cross-border data transfer regulations. Legal compliance requires specialized expertise in technology law and international data protection.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
Pharmaceutical exports involve complex regulatory frameworks including FDA approvals, patent protections, and international harmonization requirements. Legal counsel must navigate multiple regulatory regimes and intellectual property considerations.
Manufacturing and Industrial Goods
Manufacturing companies must address product liability, safety standards, and environmental compliance across multiple jurisdictions. Legal strategy should incorporate supply chain liability and product certification requirements.
Emerging Legal Trends and Future Considerations
Digital Trade and E-commerce Regulation
Digital trade provisions in bilateral agreements create new legal frameworks for e-commerce, digital services, and cross-border data flows. Companies must prepare for evolving regulatory requirements in digital trade law.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Compliance
ESG requirements are increasingly integrated into trade agreements and investment treaties. Legal compliance will require comprehensive ESG programs and sustainability reporting.
Technology Transfer and National Security
Technology transfer restrictions and national security reviews are expanding to cover broader categories of international transactions. Legal counsel must anticipate evolving restrictions and develop compliance strategies.
Conclusion: Legal Excellence in International Trade Practice
The India-US trade relationship represents a dynamic legal landscape requiring sophisticated legal analysis and proactive compliance strategies. With the India-US trade tariff dispute reshaping the regulatory environment, businesses must reassess their legal exposure and adapt to evolving compliance demands.
Our law firm’s international trade practice provides comprehensive legal services including WTO dispute resolution, customs compliance, contract negotiation, and regulatory advocacy. We combine deep legal expertise with practical business understanding to deliver effective solutions for complex trade challenges.
For businesses seeking legal guidance on India-US trade issues, tariff compliance, or international trade disputes, our experienced legal team stands ready to provide strategic counsel and effective representation. Contact our international trade law practice to discuss your specific legal needs and develop comprehensive compliance strategies.
About the Author: Aaditya Bhatt is a practicing advocate specializing in international trade law, WTO disputes, and cross-border commercial transactions. He has extensive experience advising multinational corporations, government entities, and trade associations on complex international trade matters.
Legal Disclaimer: This article provides general information about international trade law and should not be construed as legal advice. Specific legal questions should be addressed with qualified legal counsel.
Contact Information: For legal consultation on international trade matters, customs compliance, or trade dispute resolution, please contact our law firm’s international trade practice group
References
-
- Tariffs, Trade, and Troubles: Compliances for Indian companies Available at: https://disputeresolution.cyrilamarchandblogs.com/2025/04/tariffs-trade-and-troubles-compliances-for-indian-companies/
- International Trade Law: A Comparative Study Available at: https://reidellawfirm.com/international-trade-law-a-comparative-study/
- International Trade Law Available at: https://www.law.georgetown.edu/your-life-career/career-exploration-professional-development/for-jd-students/explore-legal-careers/practice-areas/international-trade-law/
- International Trade Law Research Guide Available at: https://guides.ll.georgetown.edu/c.php?g=363556&p=3915307
- WTO dispute settlement Available at: https://policy.trade.ec.europa.eu/enforcement-and-protection/dispute-settlement/wto-dispute-settlement_en
- dispute settlement procedures under wto Available at: https://www.meti.go.jp/english/report/data/2016WTO/pdf/02_19.pdf
- Customs and Tariffs: A Legal Perspective on Recent Global Trade Disputes Available at: https://www.thelearnedfriends.com/articles/customs-and-tariffs-a-legal-perspective-on-recent-global-trade-disputes
- Trump trade war faces legal challenge as businesses, states argue his tariffs exceeded his power Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/international/global-trends/trump-trade-war-faces-legal-challenge-as-businesses-states-argue-his-tariffs-exceeded-his-power/articleshow/121142650.cms
- International Trade overview Available at: https://www.whitecase.com/law/practices/international-trade
- Tariff-Related Contract Disputes: Legal Options and Advice When Trade Policies Change Available at: https://www.jchanglaw.com/post/insights-tariff-contract-disputes-legal-advice
- 10 Proven Strategies for Compliance During Tariff Disputes Available at: https://eoxs.com/new_blog/10-proven-strategies-for-compliance-during-tariff-disputes/
- impact of the trade war on businesses: understanding and mitigating risks Available at: https://www.corporatedisputesmagazine.com/impact-of-the-trade-war-on-businesses-understanding-and-mitigating-risks













